A Few New Perspectives
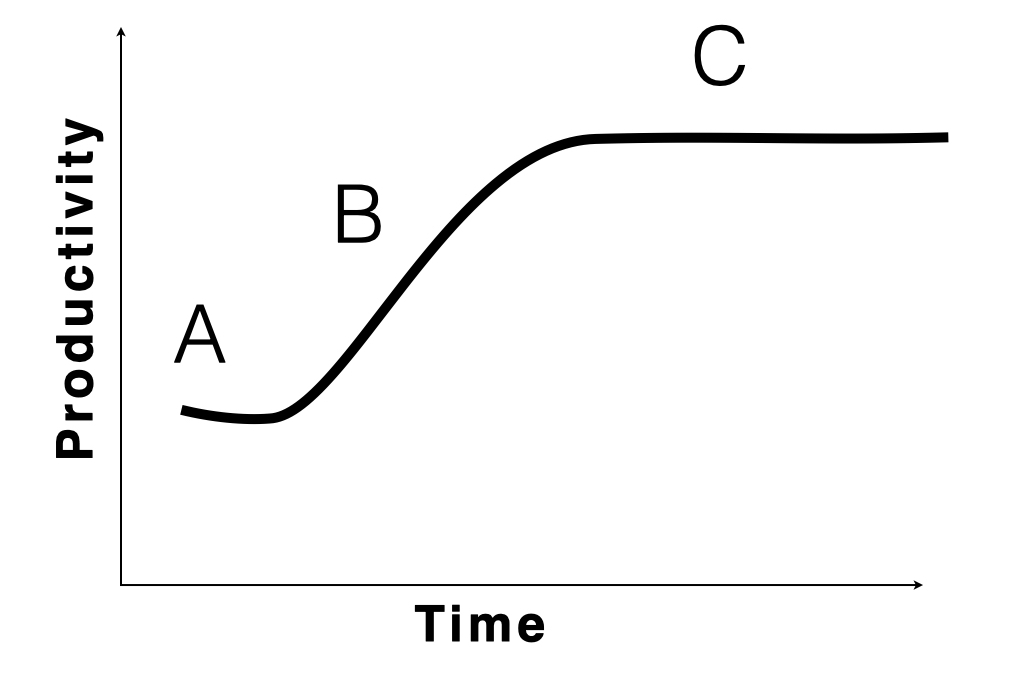
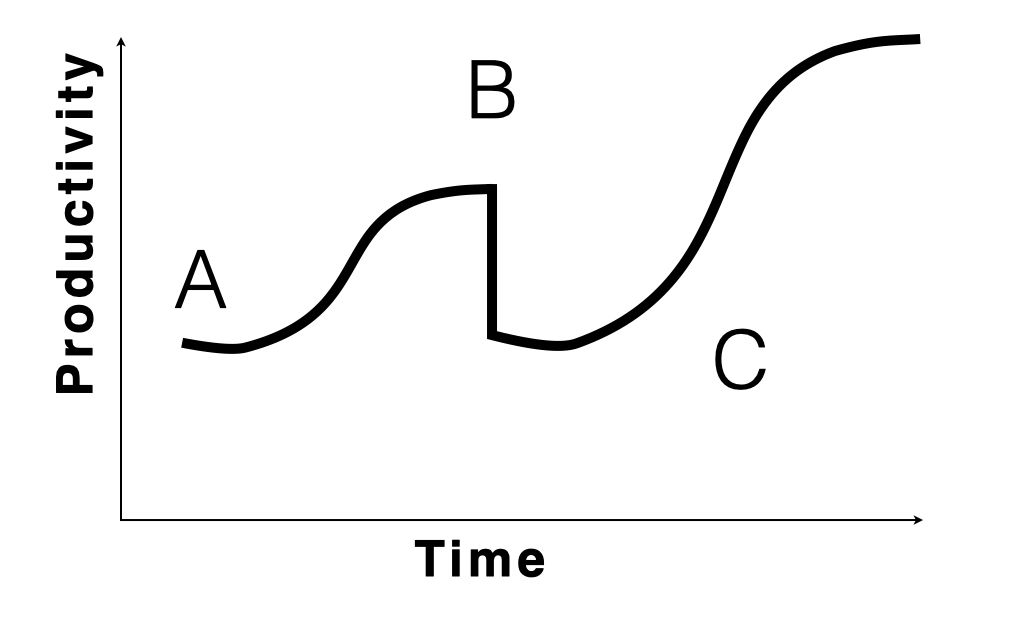
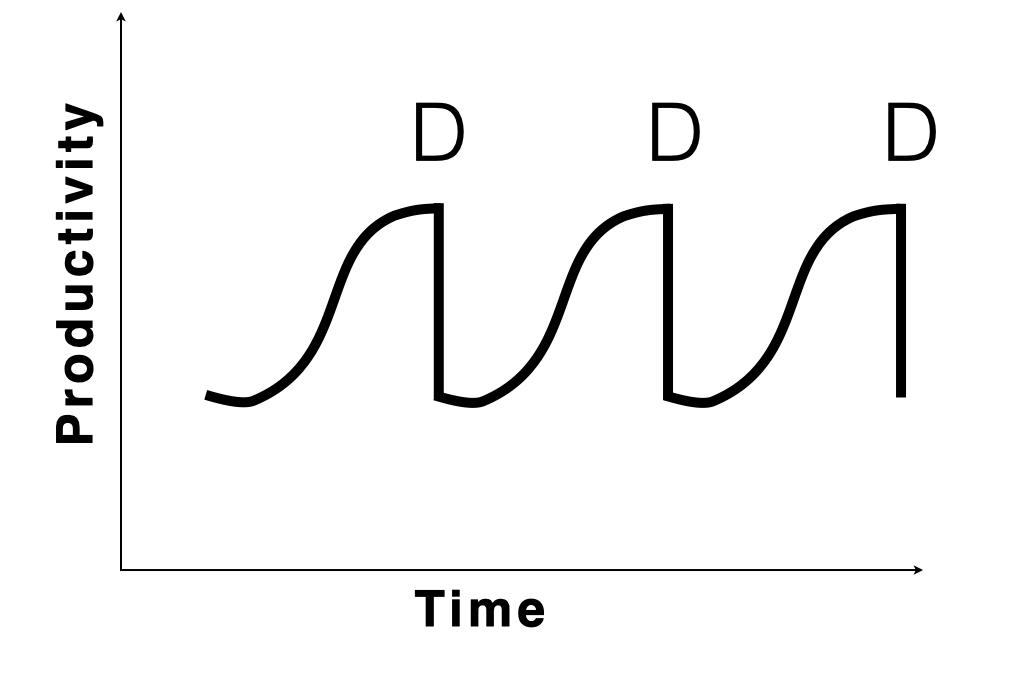
False Learning Curve
When new knowledge is required, it usually comes through learning facts, concepts and theories. Mastering these new principles, when transitioning from ‘knowledge’ to ‘know-how’ has a peculiar learning curve.
Be prepared for when it happens.
Do You Know How Your Business Operates?
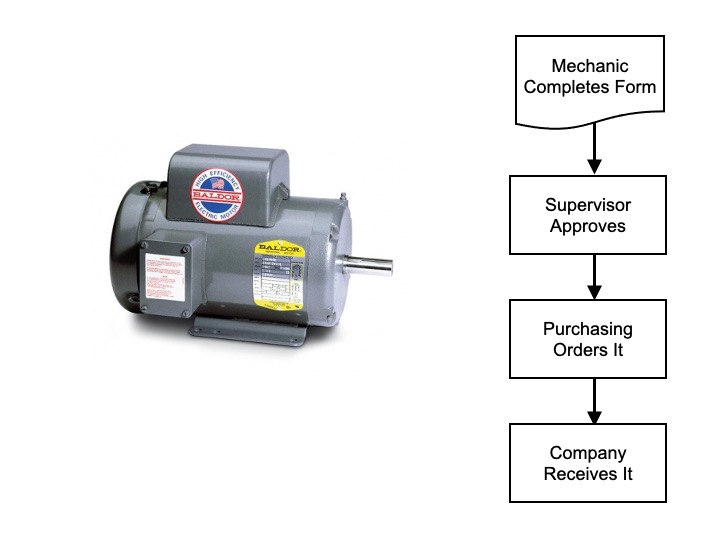
Practitioners of LEAN talk about going to the GEMBA to learn how the work is actually performed.
But what if the GEMBA crosses many decentralized location, separated by time and business functions?
Then we go ‘old school’ to attach ourselves to the work as it lurches through the organization.
Here is one example.
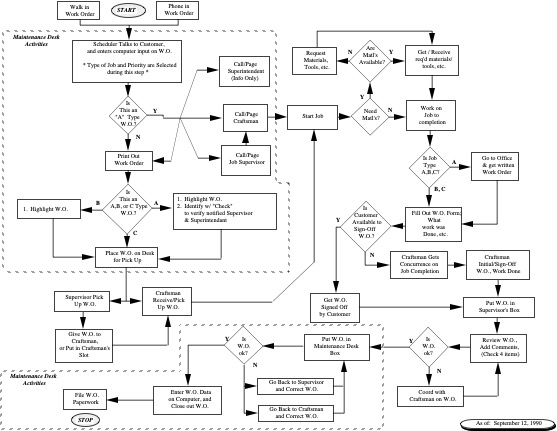
Process For Ordering An Electric Motor
Managing People
People are complex. They interact with each other, the business systems, and respond to how they are treated.
The language used throughout the organization is important. Some would say more important that actual actions.
Here are a few things to consider as a leader.
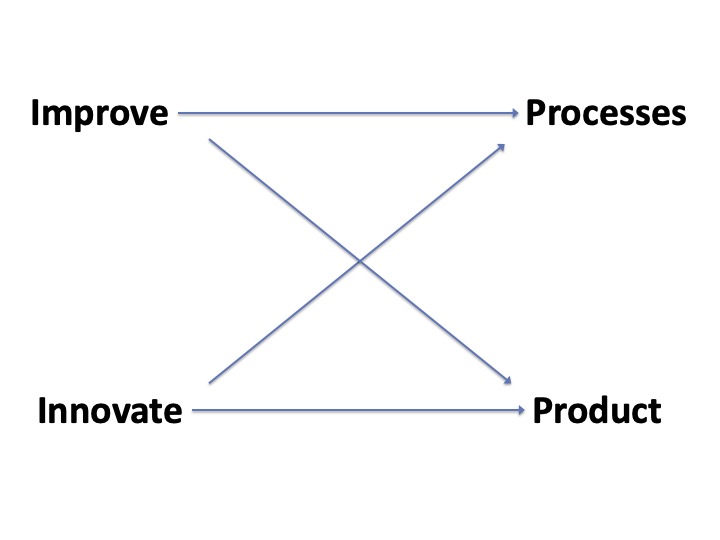
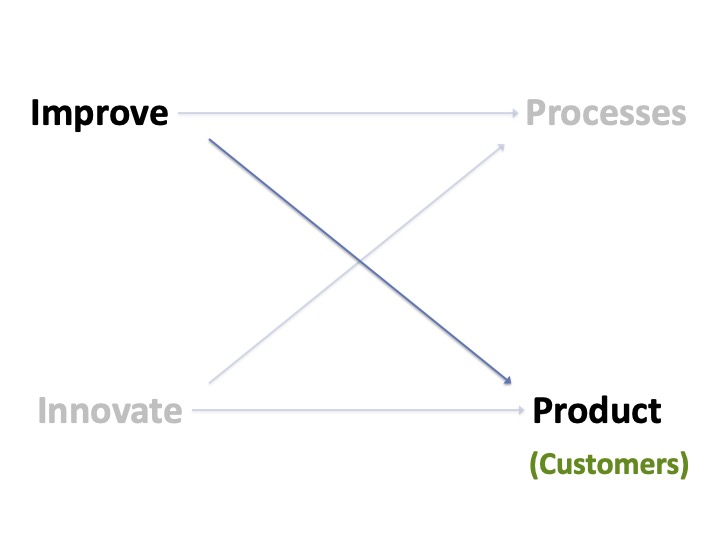
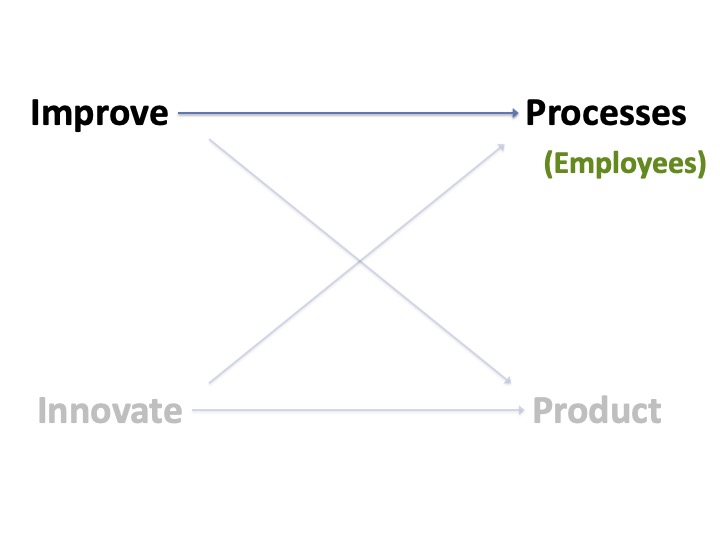
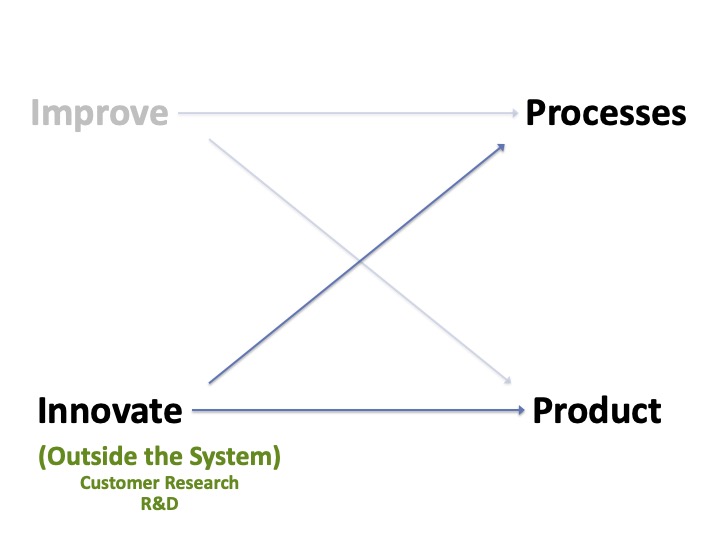
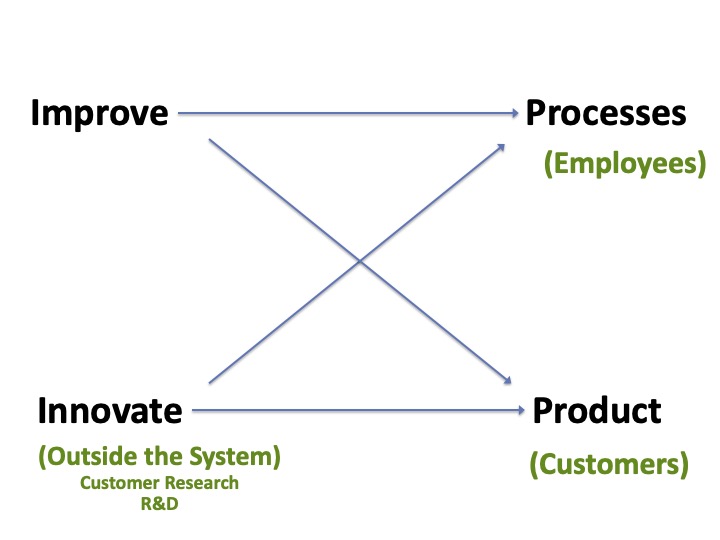
Four Opportunities For Improvement
Many want to improve something, be it the processes, working environment, or product.
However, most discussion are based on solutions the individual believe is helpful. All they have to do is convince others that their solution is the best.
Here is a model of where improvement ideas are generated.
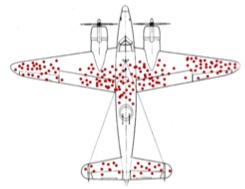
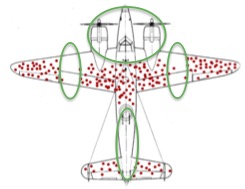
Watch Out For Logic Errors
Be careful when selecting improvement efforts. Lack of visibility can lead to false conclusions.
When failures are ignored, we can create our own optimistic belief that survivors have some special property.
Goal
Add minimal armor to increase survivability
Activity
Map damage to returning aircraft